Proficiency-Based Graduation Requirements (PBGRs) are the locally-delineated set of content knowledge and skills connected to state standards that, when supplemented with any additional locally-developed requirements, have been determined to qualify a student for earning a high school diploma. Vermont’s Education Quality Standards (EQS) require that schools’ graduation requirements be rooted in demonstrations of student proficiency, as opposed to time spent in classrooms. This requirement took effect in Vermont beginning with the graduating class of 2020.
The Vermont Portrait of a Graduate
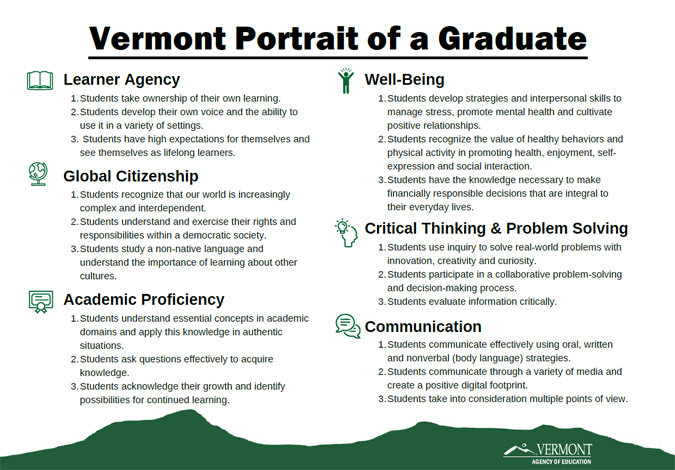
The Vermont Portrait of a Graduate (PoG) clarifies the expectations for College and Career Readiness as described in the Vermont Education Quality Standards. It specifies the cognitive, personal, and interpersonal skills and knowledge that students need to demonstrate upon graduation. The Vermont PoG was developed collaboratively by over three hundred Vermont students, community members, and educators. It can be used as a tool for reviewing and refining proficiency-based graduation requirements, as well as a guide for making instructional decisions.
- The Vermont Portrait of a Graduate with Performance Indicators
- For a more accessible version of the images below, visit the Vermont Portrait of a Graduate document.
Portrait of a Graduate Resources
The resources below are designed to support school communities in refining the Vermont Portrait of a Graduate to reflect their local context. Protocols and strategies for engaging students, educators, and community members, as well as materials for analyzing feedback, are included. By utilizing these resources, Vermont schools and communities can develop a Portrait of a Graduate that reflects their unique values while preparing students for lifelong success.
- Building Your Steering Committee
- Data Analysis: Feedback to Language
- Focus Group: Attribute Sort
- Focus Group: Chalk Talk
- Focus Group: Vision Document Sort
- Focus Group: Wagon Wheel
- Portrait of a Graduate and Personalized Learning Plan Alignment Protocol
The Vermont Framework for Proficiency Resources
Quality Criteria for Proficiency-Based Graduation Requirements, Critical Proficiencies, Priority Performance Indicators, and Proficiency Scales
The purpose of these documents is to provide criteria to evaluate and discuss the quality of Proficiency-Based Graduation Requirements (PBGRs), Critical Proficiencies (CPs), and Priority Performance Indicators (PPIs), key components of the Vermont Framework for Proficiency.
- Proficiency-Based Graduation Requirements Quality Criteria
- Critical Proficiencies Quality Criteria
- Priority Performance Indicators Quality Criteria
- Proficiency Scale Quality Criteria
Proficiency Scales and Rubrics
The purpose of the Vermont Framework for Proficiency: Developing Proficiency Scales document is to provide a process by which SU/SDs can develop proficiency scales that are connected to Priority Performance Indicators (PPIs). A proficiency scale should be designed to show a continuum of distinct levels of knowledge and skills relative to a specific performance indicator. These distinct levels are qualitative (not quantitative) and describe what the student can do (rather than not do) at each proficiency level.
-
The Unpacking Priority Performance Indicators and Proficiency Scales Template provides templates for unpacking Priority Performance Indicators and corresponding grade-level standards as well as developing proficiency scales.
The Vermont Framework for Proficiency: Proficiency Scales and Rubrics provides information about the similarities and differences between proficiency scales and rubrics. Additionally, the document explains when to use each tool and specific suggestions for classroom application.
The model proficiency scales below were developed with input from educators in the field and align with the Priority Performance Indicators in the Proficiency-Based Learning Hierarchies. As new proficiency scales are developed, they will be added to this list.
- Model Proficiency Scales for the Arts Priority Performance Indicators (Grades 9-12)
- Model Proficiency Scales for English Language Arts Priority Performance Indicators (Grades 9-12)
- Model Proficiency Scales for Mathematics Priority Performance Indicators (Grades 9-12)
- Model Proficiency Scales for Science Priority Performance Indicators (Grades 9-12)
- Model Proficiency Scales for Social Studies Priority Performance Indicators (Grades 9-12)
Proficiency-Based Graduation Requirement Content Hierarchies*
The Proficiency-Based Graduation Requirement (PBGR) Hierarchies support equity by providing a cohesive and coordinated vision of student-centered learning across Vermont schools. The hierarchies serve as a foundation for the implementation of standards adopted by the Vermont State Board of Education, Local Comprehensive Assessment Systems, flexible pathways, and personalized learning plans.
Webinar 1: Introduction to the Vermont Proficiency-Based Graduation Requirement Hierarchies provides a short introduction to the hierarchies and how they support equity in education. The video also describes how supervisory unions and districts can use the hierarchies to further support the development of their own proficiency-based graduation requirements.
Webinar 2: Understanding the Components of Proficiency-Based Graduation Requirement Hierarchies details the development process of the Proficiency-Based Requirement Hierarchies and how they can be used to support equitable learning opportunities. The video also highlights how the tool can be used to develop alignment in curricula, and the connections between transferable skills and hierarchies.
The Proficiency-Based Graduation Requirement Hierarchies Development Process explains how content specialists, in collaboration with educators from the field, developed the revised hierarchies for each of the content areas.
- Arts Proficiency-Based Graduation Hierarchy
- English Language Arts Proficiency-Based Graduation Hierarchy
- Financial Literacy Proficiency-Based Graduation Hierarchy
- Mathematics Proficiency-Based Graduation Hierarchy
- Science Proficiency-Based Graduation Hierarchy
- Social Studies Proficiency-Based Graduation Hierarchy
* The World Language Hierarchy is currently under development.
Priority Performance Indicators and Transferable Skills Connections
Transferable skills are an essential set of skills and competencies that promote the integration and application of knowledge across contexts and are critically important to success in today’s world, particularly in post-secondary programs and career readiness. These documents outline connections between the transferable skills and the Proficiency-Based Graduation Requirement (PBGR) Hierarchy, which includes the PBGR, Critical Proficiencies, and Priority Performance Indicators. It is intended to exemplify how transferable skills related to Priority Performance Assessments can be embedded into instruction and performance assessments within a unit of study.
- Arts Priority Performance Indicators and Transferable Skills Connections
- English Language Arts Priority Performance Indicators and Transferable Skills Connections
- Financial Literacy Priority Performance Indicators and Transferable Skills Connections
- Mathematics Priority Performance Indicators and Transferable Skills Connections
- Science Priority Performance Indicators and Transferable Skills Connections
- Social Studies Priority Performance Indicators and Transferable Skills Connections
K-8 Proficiency-Based Learning Hierarchies
After the PBGR Hierarchies were finalized, content specialists went through a similar process to develop Priority Performance Indicators for grades K-8. This included careful attention to vertical alignment, ensuring the skills and knowledge built in cognitive complexity across grade bands. These Proficiency-Based Learning Hierarchies can be found below, organized by content area:
Arts
- Dance K-2
- Dance 3-5
- Dance 6-8
- Music K-2
- Music 3-5
- Music 6-8
- Theater K-2
- Theater 3-5
- Theater 6-8
- Visual Arts K-2
- Visual Arts 3-5
- Visual Arts 6-8
English Language Arts (ELA)
- English Language Arts K-1
- English Language Arts 2-3
- English Language Arts 4-5
- English Language Arts 6-8
Science
Social Studies
Transferable Skills
The transferable skills identified in the Education Quality Standards can be organized in different ways. In the first document, Collaboration, Innovation, Inquiry, and Use of Technology are woven throughout the Performance Indicators. Using this model, students would need to have opportunities to demonstrate acquisition of those skills as a part of attaining their Transferable Skills Graduation Proficiencies. The Transferable Skills in the second document are the specific skills identified in EQS.
Special Education PBGR Resources
The PBGR Access Plan (PBGR-AP) was created to help educators and teams make local graduation requirements accessible for students with intensive needs. With input from stakeholders across the state, the PBGR-AP will replace the Multi-year Plan, which was based around credits/Carnegie units. The PBGR Access Plan will embrace the same spirit of accessibility that the Multi-year Plan embraced. The challenge for teachers will be to implement the PBGR Access Plan where necessary to make the graduation requirements accessible for students who are not able to access the PBGRs without some type of accommodation or modification to the PBGR Performance Indicators. A sample of a PBGR Access Plan for “Kevin” from the AOE Case Study Project and a blank template of the PBGR Access Plan that educators and teams can use for students who need help accessing the graduation requirements.
Additional Resources
Questions?
Email Pat Fitzsimmons or call (802) 828-5896.


